Most of us love knowledge contests, right? There are many applications to slake our thirst by making us answer questions coming from different professions.
This article will explain how I implemented a real-time competition app with Golang.
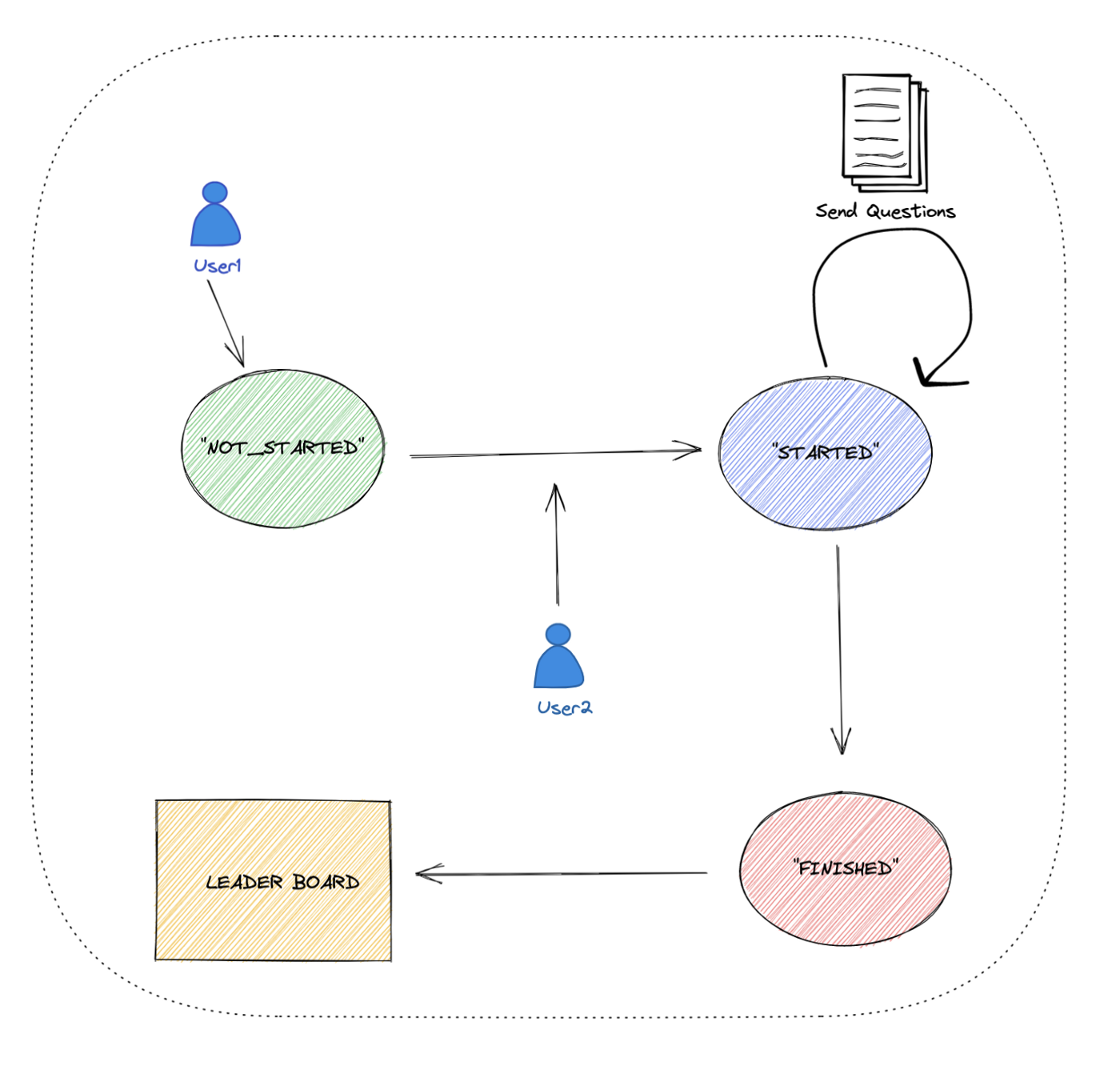
Application Flow to be implemented in Golang
There are some business rules needed to follow.
- When the number of connected users reaches two, the competition will start automatically within 3 seconds.
- There are three states in our competition. These are
NOT_STARTED,STARTED,FINISHED. - Questions have four options, and Users must answer a question within 10 seconds.
- After the competition ends, the leaderboard is shown to users to see the results of the competition.
Software Architecture Decisions
In this section, the author tries to explain why I made some decisions and try to develop some points of view on our project before we begin. This section will be like a movie spoiler. 🎥
- Websocket is the essential protocol for implementing real-time applications. It provides bidirectional communication between client and server. There are many technical articles to introduce its concepts, so I won’t go into details. I used it to send questions and get connected users’ answers.
- I used a unique id (like session-id) for each connected user. In doing so, I can easily differentiate users. In our case, we store our users’ session IDs, and our server manages read and write operations using them.
- To support concurrent read and write operations, I used
sync.Map. I used sessionID as the key and Client struct as the value shown below. The client structs consist of two fields a clientWebSocketconnection to write and read and totalScore to calculate the leaderboard.

- Broadcast is a special term to represent a method of transferring a message to all recipients simultaneously. Unfortunately, there is no broadcast method in gorilla/websocket; therefore, we will use our custom broadcast method to send messages to all users.

